Rise Of LLM Agents: How Autonomous AI Transforms Business Operations
Artificial intelligence (AI) passed several significant milestones in recent decades that transformed organizations worldwide. Advances in processing power made it possible to host models that were once technically impossible. Further advancements introduced transformer-like models, such as large language models (LLMs). LLMs demonstrated remarkable effectiveness in various industries, and by using their capabilities as intelligent agents, another significant leap forward was made.
Modern AI systems automate routine processes, such as document analysis, validation and data extraction, and information propagation. Still, an AI agent automates an entire role and adapts to the various circumstances of this role. This advancement is transformative for modern business because it presents an opportunity to delegate and facilitate operations, enhance business processes, and improve decision-making without the need to hire professionals.
With recent advancements, anyone is capable of learning these systems using natural language.

Agent-based systems: a business look
Despite the wide adoption of AI technologies, many small and large organizations struggle with rule-based systems. While such systems are relatively inexpensive for initial development and, in some cases, more interpretable, they still have flaws.
Some of these flaws are a lack of adaptability for new cases, high complexity of maintenance over time, and involvement of human teams and subject matter experts (SMEs) who place an added toll on the solution.
On the other hand, agent-based systems address these downsides. They:
- Allow for a more flexible and adaptable approach for processing standard and corner-case situations.
- Better control and maintain implemented logic, and, as a result, reduce human involvement.
- Orchestrate complex processes, emulate decision-making, and conduct error check-and-fix analysis, without writing complex business rules.
However, your business doesn’t always need to implement a high level of automation with the capabilities AI agents offer.
Below is an overview of key components used in modern business systems.
| Function calls | Multi-step chain | AI agent | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Task nature | Simple and repetitive tasks | Simple, multi-step tasks with predefined flow | Complex, multi-step tasks with unpredictable nature |
| Adaptability | Low | Moderate | High |
| Setup and maintenance cost | Low cost and minimal maintenance | Low to medium | Medium to high |
| Decision-making | Limited to hardcoded business rules with simple tasks | Limited to hardcoded business rules with complex, multi-step tasks | Autonomous decision-making |
Concept of LLM agents
An agent system consists of several components. The core is the model — the LLM. Other components are typically reasoning (logical engine of the model), memory (ability to store, recall, and update temporary context), and external tools (search, cloud functions, and APIs). The agent may also have an internal or external knowledge base.
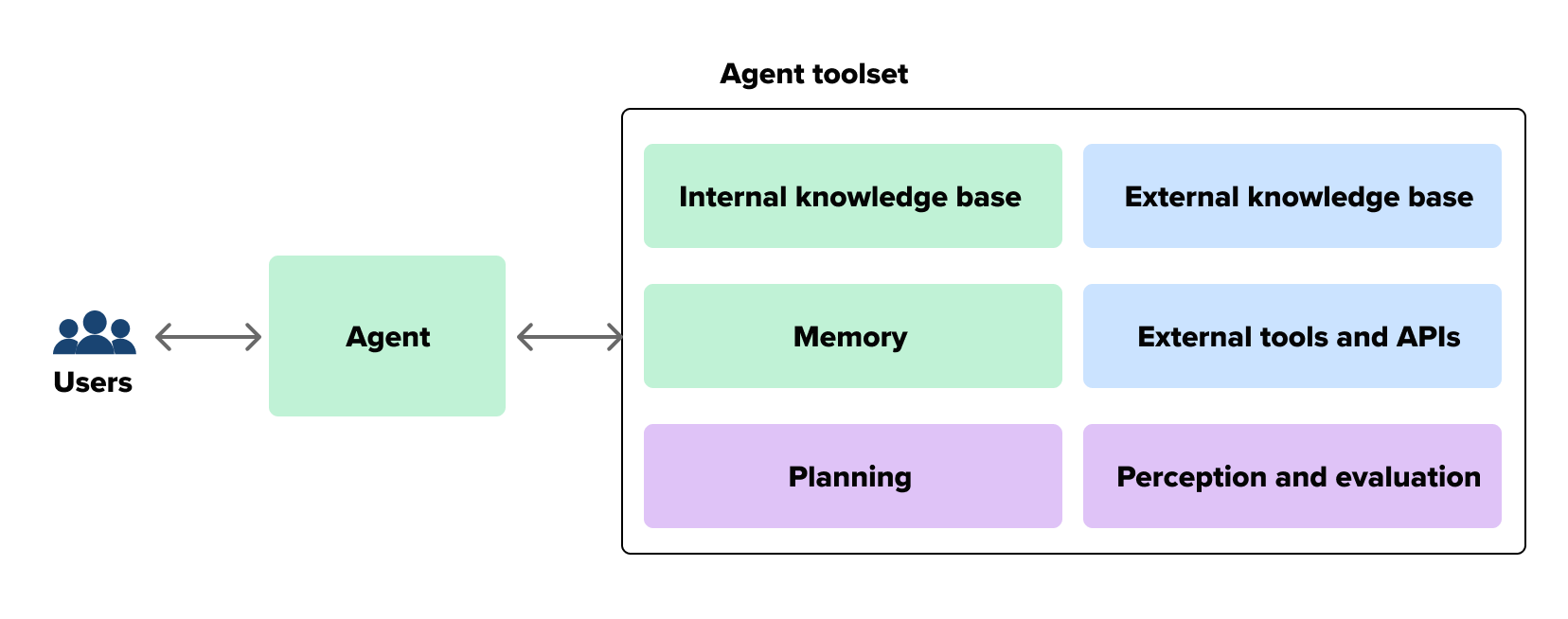
While a single agent automates a role or orchestrates several processes and tools, it still lacks adaptability to a broader area of tasks. Moreover, a single agent that’s presented with various tools may be prone to hallucinations. Therefore, more organizations lean toward orchestrating several agents in the pipeline, resulting in a multi-agent system.
Using the advanced capabilities of modern LLMs, this agent interprets and responds to user queries with fast, targeted responses. It offers valuable insights and support for a variety of business functions. It engages in natural, human-like conversations by analyzing input questions and supplied context, making it a versatile tool for many applications, such as customer service, sales, and employee assistance.
The agent's ability to retain and apply relevant information from earlier interactions or knowledge bases tailors the agent to the user's needs and requests. For business communication, it adapts tone, format, and style to meet brand guidelines. This ensures all generated content is on-brand and professional. The process of shaping the agent to meet specific needs is called prompt engineering. (If you’d like to learn more about the design of prompts, check out Master the Art of Prompt Engineering by SoftServe.)
Over time, the AI agent learns and improves from feedback or stored interactions, increasing its accuracy and performance. This "artificial evolution" enables you to handle more specific and complex inputs, adapt to specific organizational needs, and enhance productivity.
Real-world application of an AI agent
Real estate is strongly associated with automation, particularly document processing. Within this industry, many processes are tied to the lease or sale of property, each requiring the involvement of a specific set of professionals.
A core professional in property leasing and selling is the appraisal coordinator (AC). The AC plays a vital role in this process, handling document retrieval, validation, data checks, and reporting issues when they arise. With a general understanding of this role, the following is a practical case.
Recently, SoftServe designed, implemented, and delivered an agent-like system for a real estate client. This system allows for the emulation of the AC, and subsequently, many other roles. The developed system specifically mimics the efficient handling of incoming client requests, selecting the right tools from an available toolset, and processing data. Additionally, it offers the flexibility to pause and resume the process at any stage, enabling the restart of workflow or continuing seamlessly from the last completed step.
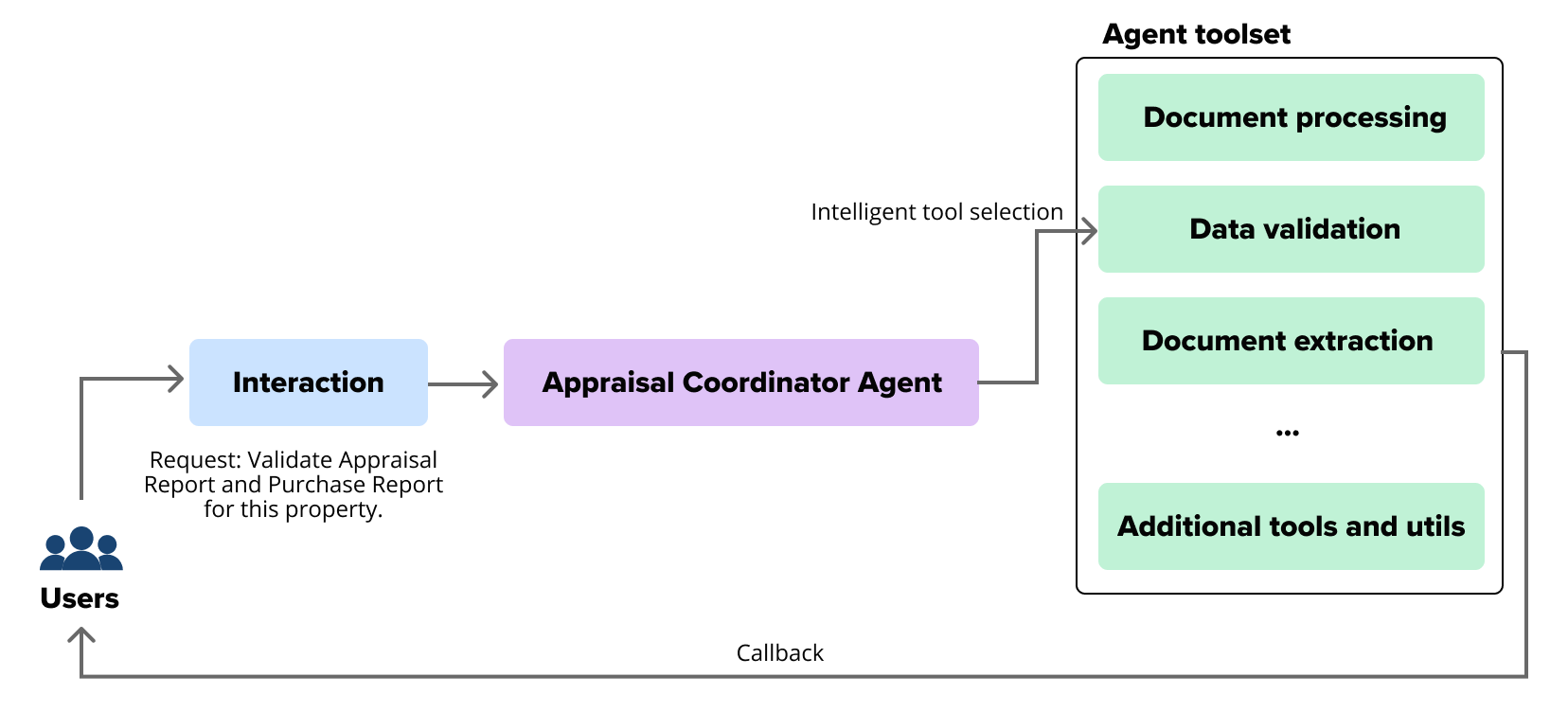
A single-agent AI system is equipped with specialized tools to effectively replicate the AC. The agent autonomously gathers required documents from various sources using document retrieval tools, making sure all mandatory documents are present. The agent then applies validation and sense check tools to verify the accuracy of the data entries and flag any inconsistencies. The agent, powered by an LLM and a set of microservice tools, halts and continues the process at any point, sends notifications, and offers more insights about the data.
Finally, the agent reports alerts to the stakeholders when issues are detected, providing a seamless, automated workflow that reduces human error and enhances efficiency across the appraisal pipeline. Humans are involved in only 20%-30% of cases, instead of, previously, 100% of cases.

Conclusion
The steady growth of AI-driven agent systems induces a new era of automation, promising to streamline operations, improve efficiency, and reduce costs across industries. With the adaptability and stored internal memory of LLMs, these agents autonomously handle complex, repetitive tasks, reducing the need for constant human intervention.
While the initial setup may require a relatively larger investment in customization and integration compared to classical, business rule-based approaches, the long-term benefits are substantial. These benefits include improved process control, greater scalability and flexibility, and enhanced engagement for both customers and employees. With advancements in AI technologies, agent systems are set to drive transformative changes, making business operations more agile and resilient.
Start transforming your business today by harnessing the power of modern AI agent systems.


